
Climate Action for Rural Economy
Climate change impacts the rural sector of India in multiple ways, including the uncertainty of the monsoon and increase in extreme events, increase in aridity in different regions, an increasing number of warm nights and days, and consequently, the health, wellbeing, livelihoods and economy. COVID-19 has exacerbated some of these stresses, especially related to erosion of farm incomes, savings and health, and wastage of produce, with marginalised groups, including landless and small farmers, and women among the worst affected. The rural sector is also a contributor to carbon emissions. There is an urgent need for emissions reduction, adaptation and resilience, and inclusive approaches for income and livelihood enhancement.

To address these concerns in the rural economy, CEE conducted studies of rural cooling needs in three village clusters in western Maharashtra, designing and testing the methodology to assess multiple cooling needs. In the year 2020, CEE conducted several commodities-specific studies in Bihar, Gujarat and Maharashtra with the objective of green recovery in the rural economy. The logical next steps evolved through learnings from these studies were initiatives of green recovery, preparing DPRs to set up renewable energy systems, processing units, marketing links and appropriate institutional structures.
Objectives
SDGs Targeted

Projects

The project aimed to study cooling demands in rural livelihood, nutrition, health, living space, mobility, vaccine cold chain, losses due to the absence or partial fulfilment of cooling needs and means through which the community is coping with these demands in designing Community Cooling Hub (CCH) proposed by Prof. Toby Peters from the University of Birmingham as a more sensible systems-level approach.
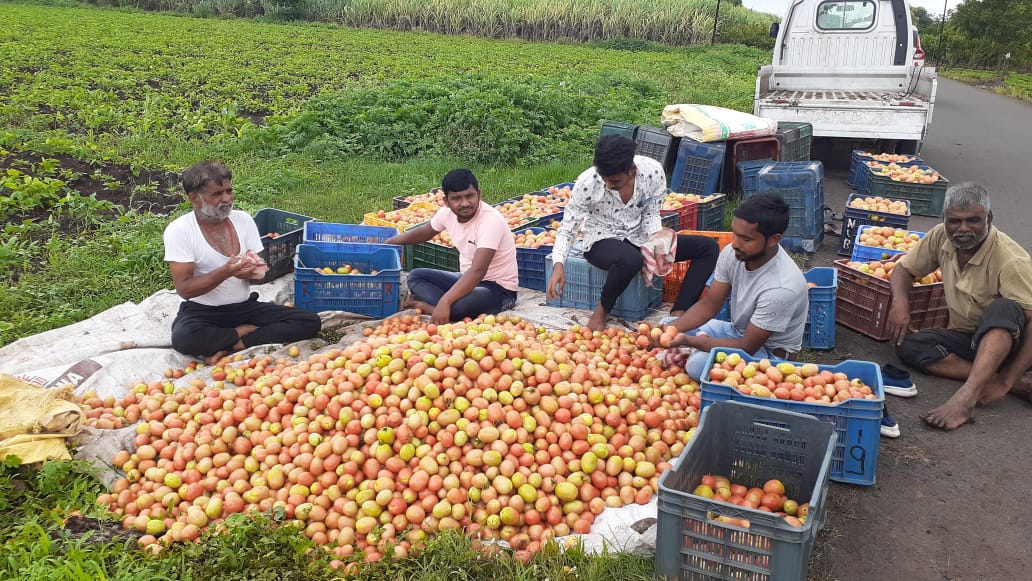 Towards Green and Socially-sound Recovery in the Farm Sector
Towards Green and Socially-sound Recovery in the Farm Sector
The study was conducted in three states (Bihar, Gujarat & Maharashtra) to develop systems overviews of the current context as well as the more sustained pre-pandemic economic patterns relevant to green recovery, enhanced livelihoods, climate resilience and reduction in carbon intensity of economic activity to identify possibilities of livelihood enhancement and renewable energy use for selected crops, fisheries, honey and eco-tourism.
 Climate Action in Rural Economy
Climate Action in Rural Economy
The CARE project was implemented in selected village clusters of three states (Bihar, Gujarat & Maharashtra) with objectives to develop CARE framework, continue site-based green recovery and harness technologies initiatives, develop communication materials and training modules for different actors, and foster collaborative, multi-stakeholder transformative approaches.
CARE Framework
CARE framework will link carbon, climate variability, resilience, natural resource base, livelihoods, inclusivity, institutions, technologies, multi-stakeholder and multi-scalar ecosystem transitions and will be useful to design and review projects, programmes and schemes at multiple stakeholder levels such as communities, Government Departments and Financing Institutions among others.
CARE Framework for the Designing and Review of Rural Economy Initiatives
Publications & Learning Resources
Case Studies
Contact
Email: [email protected]
Satish Awate, Programme Director
Email: [email protected]
Suman Rathod, Programme Director
Email: [email protected]
Preeti R. Kanaujia, Programme Director
Email: [email protected]
Established as a Centre of Excellence of the Ministry of Environment, Forest & Climate Change, Government of India.